Zibo Yunneng Kiln Technology Co. Ltd. Zibo Yunneng Kiln Technology Co. Ltd.
Free delivery samples
high quality assurance
Engineer's door-to-door guidance
lifelong technical support
Contact us+86159669653330086-533-5331887
Zibo Yunneng Kiln Technology Co. Ltd. Zibo Yunneng Kiln Technology Co. Ltd.
Free delivery samples
high quality assurance
Engineer's door-to-door guidance
lifelong technical support
Contact us+86159669653330086-533-5331887
Home -> News -> News -> Industry News ->
There are many types of refractory bricks, and the scope of application is also wide. Different types are suitable for different application industries or even different parts. What kind of refractory materials should be used for the electric furnace bottom blowing and stirring system? Direct mixing system and indirect What are the characteristics of the mixing system, what kind of refractory should be used? Due to the lack of dynamic conditions of the electric furnace, there is a large temperature difference in the molten pool of the electric furnace, the melting speed of the large scrap is slow, and the temperature difference between the two parts of the steel water is different. Increased, the composition of molten steel is not uniform. The blowing at the bottom of the electric furnace can improve the uniformity of the molten pool, eliminate the violent chemical reaction, increase the smelting speed, increase the heat transfer in the molten pool, and quickly melt the large scrap and the added alloy, which can shorten the smelting cycle. It saves power consumption, reduces tapping temperature, accelerates slag foaming, and reduces production costs. Therefore, electric bottom blowing has been well developed in actual smelting. There are two types of bottom-blowing agitation systems currently in use: one is the type of direct agitation system, and the other is the type of indirect agitation system: the refractory material for the electric furnace bottom-blowing agitation system is shown in Figure 1.
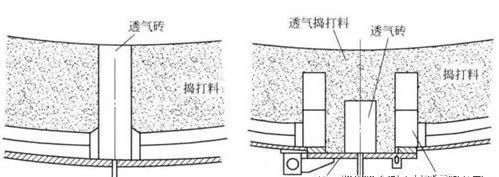
The refractory materials used in the direct mixing system are permeable bricks and seat tiles and ramming materials. Most of the ventilated bricks are made by embedding steel pipes in magnesia carbon bricks, commonly known as magnesium carbon permeable bricks.
Features of direct mixing system:
(1) The permeable brick is damaged due to direct contact with molten steel;
(2) It needs to be replaced in a short time, for example, every three weeks, and the operating erosion rate is about 0.5mm per hour;
(3) The gas introduction is locally concentrated in the molten steel molten pool, and vigorous stirring is formed in a small range;
(4) The molten steel is partially covered by slag and absorbs nitrogen;
(5) The gas must be continuously supplied. In the standard state, the flow rate of each ventilating brick is about 3~5m3/h, otherwise it will easily cause the venting of the ventilating brick.
Indirect agitation systems typically have a layer of breathable ramming material on top of the gas permeable element. The venting element can be either a permeable brick or a venting tube.
Characteristics of the indirect mixing system:
(1) The ventilated brick is covered by the ventilated ramming material, and the erosion is slow, so the entire furnace can be maintained, even for one year, and only the bottom of the furnace needs regular maintenance;
(2) The gas enters the molten steel pool in a wide range, is widely distributed, and has a large area of light bubbles;
(3) This device cannot open the slag from around the taphole;
(4) The air supply can be interrupted. In the standard state, the typical flow rate is 5~7m3/breathable brick.

Relevant Product Display
 Non-stick aluminium castable
Non-stick aluminium castable
 Mullite high strength explosion-proof castable G-16K
Mullite high strength explosion-proof castable G-16K
 Wear-resistant refractory castable D-17m
Wear-resistant refractory castable D-17m
 High temperature adhesive
High temperature adhesive
Relevant information
Hotline